


Next: 2.4.3 Common kernel functions
Up: 2.4 Kernel PCA
Previous: 2.4.1 Feature extraction
2.4.2 Centering in feature space
So far, we have assumed that
{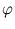 (
(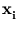 )} has zero mean, which is usually not fulfilled. Therefore, the formalism needs to be adjusted (Schölkopf et al., 1998b). The following set of points will be centered:
)} has zero mean, which is usually not fulfilled. Therefore, the formalism needs to be adjusted (Schölkopf et al., 1998b). The following set of points will be centered:
The above analysis holds if the covariance matrix is computed from

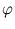 (
(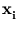 ). Thus, the kernel matrix
Kij =
). Thus, the kernel matrix
Kij = 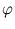 (
(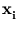 )T
)T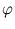 (
(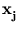 ) needs to be replaced by
) needs to be replaced by
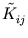 =
= 
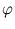 (
(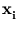 )T
)T
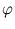 (
(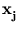 ). Using (2.31),
). Using (2.31), 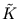 can be written as,
can be written as,
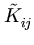 |
= |
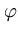 ( (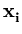 )T )T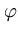 ( (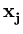 ) - ) - 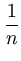 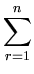 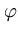 ( (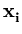 )T )T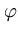 ( (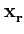 ) - ) - 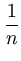 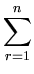 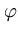 ( (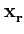 )T )T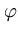 ( (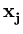 ) ) |
|
| |
+ |
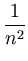 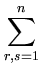 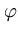 ( (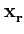 )T )T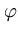 ( (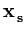 ) ) |
|
| |
= |
Kij - 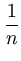 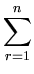 Kir - Kir - 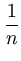 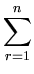 Krj + Krj + 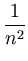 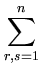 Krs . Krs . |
(2.32) |
Therefore, we can evaluate the kernel matrix for the centered data using the known matrix 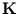 . For the remainder of this thesis, I denote with
. For the remainder of this thesis, I denote with
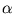 the eigenvectors of
the eigenvectors of
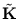 instead of
instead of 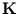 , and they are normalized according to (2.29) using the eigenvalues of
, and they are normalized according to (2.29) using the eigenvalues of
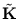 . The principal components are
. The principal components are
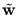 =
= 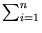
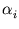

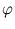 (
(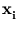 ).
).



Next: 2.4.3 Common kernel functions
Up: 2.4 Kernel PCA
Previous: 2.4.1 Feature extraction
Heiko Hoffmann
2005-03-22
![]() (
(![]() )} has zero mean, which is usually not fulfilled. Therefore, the formalism needs to be adjusted (Schölkopf et al., 1998b). The following set of points will be centered:
)} has zero mean, which is usually not fulfilled. Therefore, the formalism needs to be adjusted (Schölkopf et al., 1998b). The following set of points will be centered: